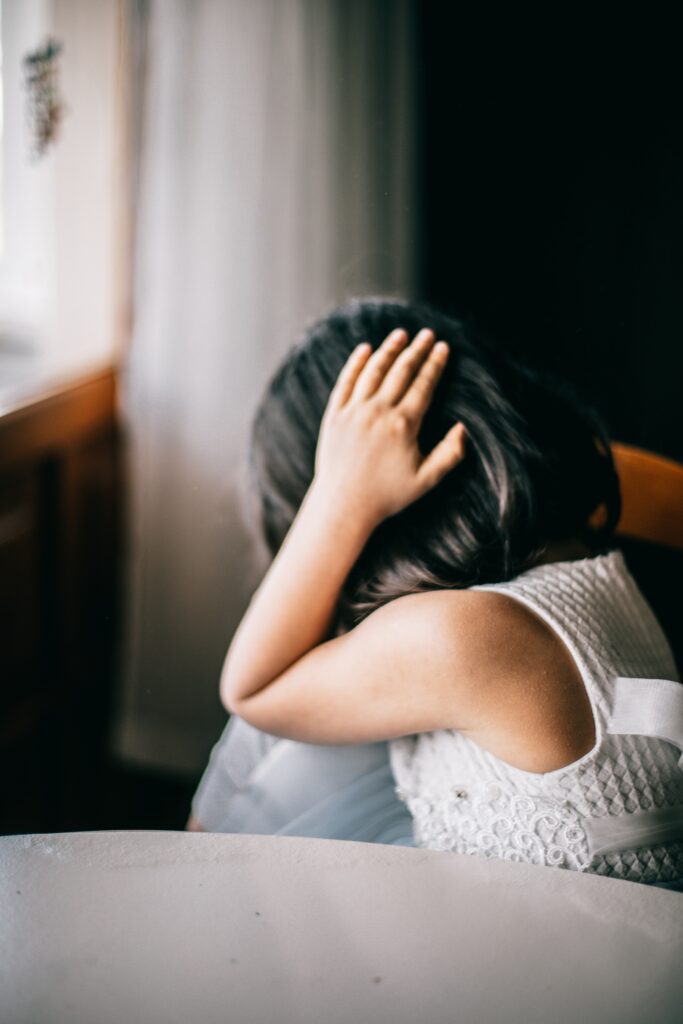
Anxiety is a normal part of life, but when it becomes excessive and interferes with a child’s ability to function, it can be considered a mental health disorder. Children with anxiety often experience fear, worry, and nervousness in response to everyday situations. This can lead to physical symptoms such as headaches, stomachaches, and trouble sleeping.
Anxiety disorders are the most common mental health disorder among children and adolescents. According to the National Institute of Mental Health, an estimated 25% of children and adolescents experience an anxiety disorder at some point in their lives. These disorders can take many forms, including generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, separation anxiety disorder, and specific phobias.
Generalized anxiety disorder is characterized by excessive and unrealistic worry about everyday situations. Children with this disorder may worry about things such as school, family, and friends. They may also have trouble sleeping and have physical symptoms such as stomachaches and headaches.
Social anxiety disorder is characterized by excessive fear of social situations. Children with this disorder may have trouble making friends, participating in class, and speaking in public. They may also experience physical symptoms such as sweating, shaking, and blushing.
Separation anxiety disorder is characterized by excessive fear of being separated from a parent or caregiver. Children with this disorder may have trouble sleeping away from home, attending school, or going to daycare. They may also experience physical symptoms such as stomachaches and headaches.
Specific phobias are characterized by excessive fear of specific objects or situations. Children with specific phobias may have trouble participating in activities that involve the object or situation they are afraid of. For example, a child with a phobia of dogs may have trouble playing outside or going to a friend’s house if there is a dog present.
There are many factors that can contribute to the development of anxiety disorders in children. These include genetic predisposition, stress, and traumatic experiences. Children who have a family history of anxiety or other mental health disorders are more likely to develop an anxiety disorder. Stressful events such as the death of a loved one, divorce, or moving to a new home can also contribute to the development of anxiety disorders in children.
Trauma can also play a role in the development of anxiety disorders in children. Children who have experienced abuse, neglect, or other traumatic events may be more likely to develop an anxiety disorder.
There are several treatment options available for children with anxiety disorders. The most common treatment is cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). CBT is a type of therapy that helps children learn to change their thoughts and behaviors in order to reduce their anxiety. This type of therapy can be done individually or in a group setting.
Medication is also sometimes used to treat anxiety disorders in children. Antidepressants such as fluoxetine (Prozac) and sertraline (Zoloft) are commonly used to treat anxiety disorders in children. These medications can help reduce symptoms of anxiety, but they can also have side effects.
Another treatment option for children with anxiety disorders is mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR). MBSR is a type of therapy that helps children learn to focus on the present moment and to be more aware of their thoughts and feelings. This type of therapy can be done individually or in a group setting.
It is important for parents and caregivers to be aware of the signs of anxiety in children. If a child is experiencing excessive fear, worry, or nervousness in response to everyday situations, it is important to seek help. Children with anxiety disorders can benefit from treatment, and early intervention can help prevent the disorder from becoming more severe.
Though anxiety is a normal part of life, but when it becomes excessive and interferes with a child’s ability to function, it is considered a mental health disorder. Children with anxiety disorders may experience fear, worry, and nervousness in response to everyday situations, leading to physical symptoms such as headaches, stomachaches, and trouble sleeping. There are several types of anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, separation anxiety disorder, and specific phobias. These disorders can develop due to a combination of genetic predisposition, stress, and traumatic experiences.
It is also paramount for caregivers to be aware of the signs of anxiety in children and seek help if necessary. Treatment options include cognitive-behavioral therapy, medication, and mindfulness-based stress reduction. Early intervention can help prevent the disorder from becoming more severe, allowing children to live happy, healthy lives.